Understanding the Average Health Insurance Cost: Factors, Types, Disparities, and Strategies
Exploring the realm of average health insurance cost, this comprehensive guide delves into the various factors, types of plans, regional differences, and strategies to manage expenses. Get ready to uncover the intricacies of health insurance costs and how they impact individuals and families alike.
Factors influencing average health insurance cost
When it comes to determining the average cost of health insurance, several factors play a significant role in shaping the premiums that individuals or families pay. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions when selecting a health insurance plan.
Demographics
Demographic factors such as age, location, and family size can have a direct impact on health insurance costs. Older individuals typically face higher premiums due to increased healthcare needs, while the location can affect costs based on regional healthcare expenses and regulations.
Family size also plays a role, as more family members mean a higher likelihood of medical expenses.
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices like smoking, exercise habits, and diet can influence health insurance costs. Smokers often face higher premiums due to the increased health risks associated with smoking. On the other hand, individuals with healthy lifestyle habits may qualify for discounts or lower premiums, as they are less likely to require extensive medical treatment.
Pre-existing Conditions
The presence of pre-existing conditions can significantly impact health insurance expenses. Individuals with chronic illnesses or health conditions may face higher premiums or exclusions from coverage for specific treatments. Insurers consider pre-existing conditions as a risk factor, leading to increased costs for individuals with such medical histories.
Types of health insurance plans and their cost differences
When it comes to health insurance, there are various types of plans available, each with its own cost structure. Understanding the differences between these plans can help individuals and families make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage.
HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations)
- HMOs typically have lower premiums compared to other types of plans.
- Members are required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) and get referrals to see specialists.
- Out-of-network coverage is limited or not covered, which can result in higher out-of-pocket costs.
PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations)
- PPOs offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers without needing a referral.
- Premiums are usually higher compared to HMOs, but members have the option to see out-of-network providers at a higher cost.
- Out-of-pocket costs may be lower when using in-network providers.
High-Deductible Health Plans
- High-deductible plans have lower premiums but come with higher deductibles that must be met before insurance coverage kicks in.
- These plans are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) to help cover out-of-pocket costs.
- Individuals and families with high-deductible plans may have to pay more upfront for healthcare services until they reach their deductible.
Regional disparities in average health insurance cost
In the United States, the cost of health insurance can vary significantly depending on the geographic location. Factors such as the cost of living, healthcare provider availability, and state regulations can all impact the average health insurance premiums in different regions.
Urban vs. Rural Areas
- Urban areas tend to have higher health insurance premiums compared to rural areas. This is often due to higher healthcare costs and a greater demand for medical services in urban centers.
- Rural areas, on the other hand, may have lower insurance premiums but could face challenges related to limited access to healthcare providers and facilities.
- Providers in rural areas may have lower reimbursement rates from insurance companies, which can affect the overall cost of health insurance for residents.
State-by-State Comparison
- States like New York, Massachusetts, and Alaska typically have higher health insurance costs compared to states like Utah, Iowa, and South Dakota.
- Differences in state regulations, healthcare infrastructure, and population health can all contribute to the varying insurance premiums across different states.
- States with a higher prevalence of chronic conditions or a larger aging population may see increased health insurance costs due to higher utilization of medical services.
Strategies for lowering average health insurance cost
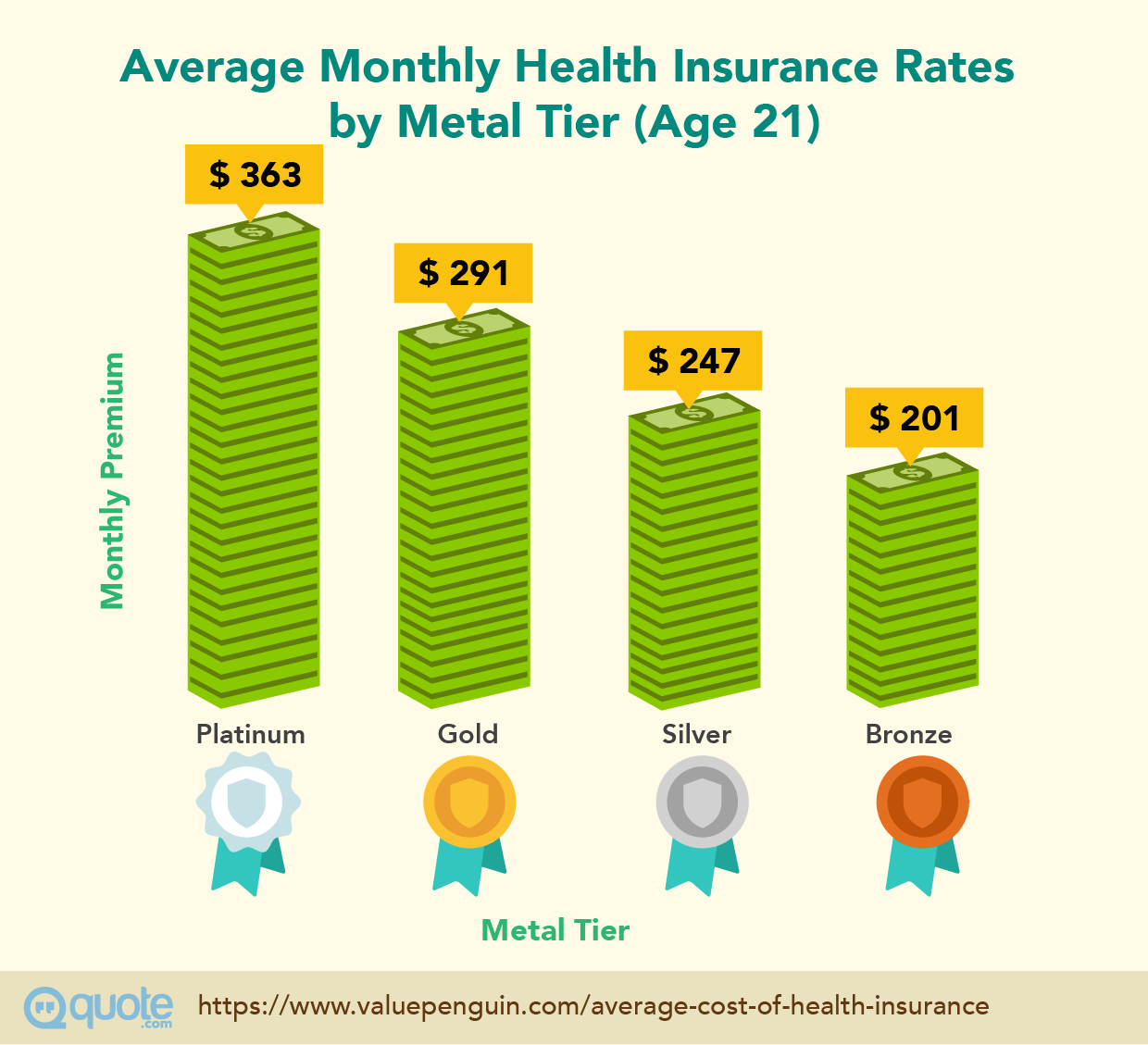
When it comes to managing healthcare costs, there are several strategies that individuals can consider to lower their average health insurance expenses without compromising coverage. From utilizing health savings accounts (HSAs) to focusing on preventive care and negotiating with insurance providers, these approaches can help individuals save money while maintaining essential healthcare coverage.
Utilize Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
Health savings accounts (HSAs) can be a valuable tool in managing healthcare expenses. By setting aside pre-tax dollars for qualified medical expenses, individuals can lower their taxable income and save money on healthcare costs. HSAs are particularly beneficial for those with high-deductible health plans, offering a way to cover out-of-pocket expenses while enjoying tax advantages.
Focus on Preventive Care and Wellness Programs
Investing in preventive care and wellness programs can help individuals lower their overall healthcare expenses in the long run. By prioritizing regular check-ups, screenings, and healthy lifestyle choices, individuals can detect health issues early, prevent costly medical treatments, and maintain optimal health.
Many insurance plans offer incentives for participating in wellness programs, making it a cost-effective way to stay healthy.
Negotiate with Insurance Providers
When it comes to lowering health insurance costs, don't be afraid to negotiate with your insurance provider. Many insurers are willing to work with policyholders to adjust premiums based on factors like age, health status, and coverage needs. By exploring different coverage options, adjusting deductibles, or seeking discounts, individuals can potentially lower their monthly premiums and save money on healthcare expenses.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, navigating the landscape of average health insurance cost involves understanding the multifaceted elements that contribute to pricing, selecting the right plan that suits your needs, and exploring avenues to reduce expenses without compromising coverage. Stay informed, stay proactive, and make informed decisions regarding your health insurance to secure a healthy financial future.