Exploring Government Health Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide
Delving into the realm of government health insurance, this paragraph sets the stage for a deep dive into the intricacies and significance of this crucial aspect of healthcare.
The following paragraphs will shed light on the concept, types, funding, coverage, and benefits of government health insurance programs.
Overview of Government Health Insurance

Government health insurance refers to healthcare coverage provided by the government to its citizens. It aims to ensure that individuals have access to essential medical services without facing financial hardship.
Main Objectives of Government Health Insurance Programs
Government health insurance programs have several key objectives:
- Ensure universal healthcare coverage for all citizens, regardless of their socio-economic status.
- Protect individuals from high out-of-pocket expenses for medical treatments.
- Promote preventive healthcare measures to reduce the burden of disease in the population.
- Improve overall health outcomes and life expectancy by providing timely and quality healthcare services.
Importance of Government Health Insurance in Providing Healthcare Access
Government health insurance plays a crucial role in providing healthcare access to the population:
- It ensures that individuals can seek medical care when needed without worrying about the cost.
- By covering a wide range of medical services, government health insurance promotes early detection and treatment of illnesses.
- It helps reduce health disparities by ensuring that even marginalized populations have access to healthcare services.
- Government health insurance contributes to the overall well-being of society by keeping the population healthy and productive.
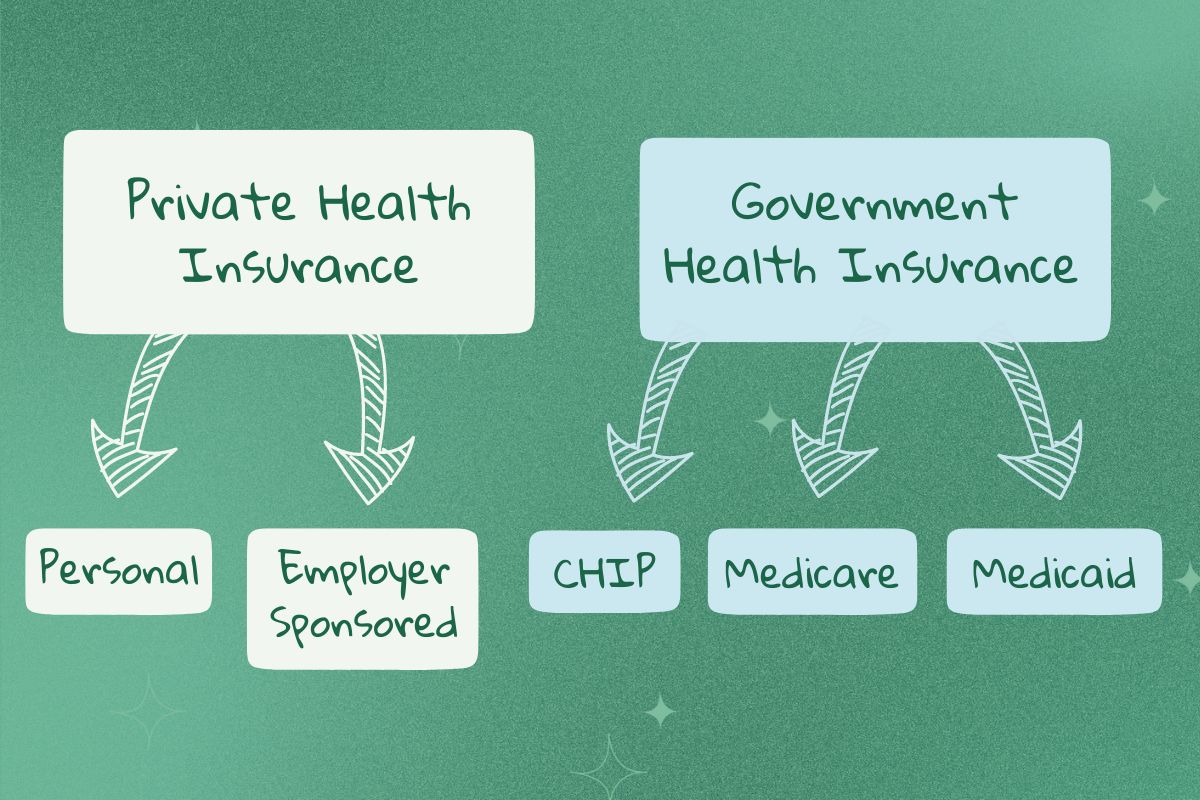
Types of Government Health Insurance Programs
Government health insurance programs vary globally, offering different models to ensure access to healthcare for citizens. These programs play a crucial role in promoting public health and well-being by providing financial support for medical services. Let's explore some of the common types of government health insurance programs and their impact on healthcare outcomes.
Single-Payer System
In a single-payer system, the government is the sole entity responsible for financing healthcare services for all residents. Countries like Canada and the United Kingdom have successfully implemented this model, providing universal coverage to their citizens. This system simplifies the healthcare process by eliminating the need for multiple insurance providers and streamlining administrative costs.
Multi-Payer System
Contrastingly, a multi-payer system involves multiple insurance providers, both public and private, offering coverage to citizens. Germany and France are examples of countries with successful multi-payer systems, where individuals can choose their insurance provider. This model allows for competition among insurers, potentially leading to better quality of care and service delivery.
National Health Insurance
Under a national health insurance system, the government mandates that all citizens have health insurance, but it does not directly provide healthcare services. Instead, it acts as a regulator and oversees the financing of healthcare through contributions from employers and employees.
Japan's healthcare system is a prominent example of a successful national health insurance program, ensuring comprehensive coverage for all residents.
Impact on Public Health Outcomes
Government health insurance programs have a significant impact on public health outcomes by ensuring that individuals have access to necessary medical care without financial barriers. These programs contribute to lower mortality rates, increased life expectancy, and improved overall health outcomes for populations
By promoting preventive care and early intervention, government health insurance plays a crucial role in maintaining the well-being of citizens.
Funding and Sustainability
Government health insurance programs are typically funded through a combination of sources, including general tax revenues, specific health insurance premiums, and contributions from employers and employees. These programs aim to provide affordable healthcare coverage to a large segment of the population, especially those who may not have access to private health insurance.
Funding Sources
- General tax revenues: Governments allocate a portion of their overall budget towards funding health insurance programs to ensure that essential healthcare services are accessible to all citizens.
- Health insurance premiums: Some government health insurance programs require individuals to pay premiums based on their income level. These premiums help offset the costs of providing healthcare services.
- Employer and employee contributions: In some cases, employers and employees contribute towards government health insurance programs through payroll deductions. These contributions help sustain the financial stability of the program.
Challenges in Sustainability
- Rising healthcare costs: As medical advancements and technologies progress, the cost of healthcare services continues to increase, putting pressure on government health insurance programs to sustainably fund these services.
- Aging population: With an aging population, there is a greater demand for healthcare services, leading to increased strain on government health insurance programs to meet the needs of a growing demographic.
- Political and economic instability: Changes in government leadership and economic downturns can impact the funding and sustainability of government health insurance programs, creating uncertainty for beneficiaries.
Strategies for Financial Viability
- Implementing cost-containment measures: Governments can explore strategies to control healthcare costs, such as promoting preventive care, negotiating lower drug prices, and reducing administrative expenses.
- Diversifying funding sources: Governments can consider diversifying funding sources for health insurance programs to reduce reliance on a single revenue stream and ensure financial stability in the long run.
- Public-private partnerships: Collaborating with private healthcare providers and insurers can help enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of government health insurance programs, ensuring better outcomes for beneficiaries.
Coverage and Benefits
Government health insurance programs typically offer a wide range of coverage and benefits to ensure access to essential healthcare services for all eligible individuals. These programs aim to provide financial protection against high medical costs and promote better health outcomes for the population.
Coverage and Benefits Offered
- Preventive care services such as vaccinations, screenings, and counseling
- Emergency medical treatment and hospitalization
- Doctor visits and specialist consultations
- Prescription medications
- Mental health services and substance abuse treatment
- Maternity care and newborn care
- Rehabilitative services and devices
Coverage Eligibility Determination
Government health insurance schemes typically determine coverage eligibility based on factors such as income level, age, disability status, and citizenship or residency status. Eligibility criteria may vary depending on the specific program and the target population it serves.
Role in Improving Healthcare Equity
Government health insurance plays a crucial role in improving healthcare equity by ensuring that all individuals, regardless of their socio-economic status, have access to necessary medical services without facing financial hardship.
By providing coverage to vulnerable populations and offering essential benefits, these programs help reduce disparities in healthcare access and outcomes, ultimately contributing to a more equitable healthcare system.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, government health insurance plays a vital role in ensuring healthcare access and equity, with its impact reaching far and wide. This guide aims to provide a holistic view of the landscape of government health insurance and its implications on public health.