Understanding Group Health Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide
Group health insurance has become an essential part of many organizations' benefits packages. By offering group health insurance, employers can provide their employees with access to quality healthcare services at affordable rates. In this guide, we will delve into the world of group health insurance, exploring its definition, types, workings, coverage, costs, advantages and disadvantages, administration, and trends.
As you journey through the following sections, you will gain a deeper understanding of group health insurance, enabling you to make informed decisions about your organization's benefits offerings.
Definition of Group Health Insurance
Group health insurance is a type of insurance coverage that provides access to healthcare services for a group of people, typically consisting of employees of a company or members of an organization. In this arrangement, the insurance policy is purchased by the employer or organization and offered to eligible participants as a benefit.
This is distinct from individual health insurance, where a policy is purchased by and for a single person or family.
Parties Involved in Group Health Insurance
The primary parties involved in group health insurance include the insurer, the policyholder (which can be an employer or an organization), and the plan participants, who are usually employees or members of a group.
Benefits of Group Health Insurance Over Individual Health Insurance
Group health insurance offers several advantages compared to individual health insurance options, including:
-
Cost savings: By pooling the risk of a group, insurance providers can offer more affordable premiums compared to individual policies.
-
Wider coverage: Group health insurance often includes more services and benefits compared to individual plans, ensuring participants receive comprehensive coverage.
-
Easier enrollment: Obtaining group health coverage is typically less complex than applying for individual policies, with reduced documentation and faster approvals.
Types of Group Health Insurance
Group health insurance is an essential aspect of employee benefits packages, offering medical coverage to groups of individuals under a single policy. Various types of group health insurance plans are available, each with unique features and advantages. This guide explores five common group health insurance plans: Fully Insured Plans, Self-Funded Plans, Level-Funded Plans, Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs).
Fully Insured Plans
Fully Insured Plans are the most conventional group health insurance type, wherein an employer pays a fixed premium to the insurance company for the policy's duration, and the carrier assumes all risk and covers any claims. These plans' simplicity allows for a wide range of coverage options and ease of management.
However, they can become costly, especially if an employer's workforce incurs high medical claims.
Self-Funded Plans
Unlike Fully Insured Plans, Self-Funded Plans place the responsibility on the employer for covering claims. An employer can pay claims directly or through a third-party administrator, and they can purchase stop-loss coverage for high-dollar claims. This arrangement often results in lower costs for employers if the claims are lower than expected.
However, self-funded plans might be riskier for smaller companies due to the uncertainty of potential medical claims.
Level-Funded Plans
Level-Funded Plans are a hybrid of Fully Insured and Self-Funded Plans. Employers pay a fixed monthly amount based on estimated annual claims, covering the administrative and insurance costs. At the end of the policy term, the employer receives a refund for any unexpended funds or may be required to pay more if the claims exceed the estimate.
These plans offer the financial predictability of Fully Insured Plans with the potential cost savings of Self-Funded Plans.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
HMOs are a type of managed care organization with strict provider networks. Employees are limited to using healthcare providers within the network, and referrals are usually needed for specialist services. While HMOs offer less flexibility, they can offer lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
Additionally, HMOs typically feature robust preventive care programs.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)
PPOs are a more flexible managed care option than HMOs. Employees can choose in-network or out-of-network providers, but using in-network options results in lower costs. PPOs offer wider network coverage and fewer limitations for specialist services compared to HMOs, which brings higher premiums than HMOs but still maintains a significant cost advantage over Fully Insured Plans.
When choosing a group health insurance plan, employers must consider factors such as workforce size, risk tolerance, and preferred cost-sharing arrangements. Balancing coverage options, cost, and employee satisfaction is crucial for a successful benefits package.
How Group Health Insurance Works
Obtaining group health insurance involves various steps, with the employer or the organization playing a crucial role in the process. Regular contributions from both the employer and employees are essential to ensuring the group health insurance plan remains active and beneficial for all members.
Process of Obtaining Group Health Insurance
A group health insurance policy is generally initiated by an employer or organization, seeking to provide health coverage for their employees or members. Here are the primary steps involved in the process:
1. Identify the group health insurance needs
Before approaching insurers, it's vital to understand the group's requirements in terms of coverage, deductibles, co-pays, and more.
2. Research and compare group health insurance options
Look into different insurance providers and plans. Assess the costs, benefits, and limitations of each option.
3. Select a group health insurance plan
After research, decide on the most suitable plan for the group. Consider the group's demographics, overall health, and financial situation when making the decision.
4. Negotiate terms and pricing
Work with the selected insurer to finalize the plan and pricing. This may involve discussing the group size, risk factors, and coverage options.
5. Enroll employees or members
Provide detailed information about the plan and enrollment process. Typically, this occurs during an open enrollment period.
6. Begin coverage
Once all enrollments are complete, the group health insurance plan becomes active, and members can access benefits as Artikeld in the policy.
Role of Employer/Organization
The employer or organization acts as the primary liaison between the insurance company and the group members. Their responsibilities include:
- Identifying and prioritizing group health insurance needs.
- Researching and comparing insurance providers.
- Negotiating terms and pricing.
- Facilitating enrollment and educating members.
- Making regular contributions and managing plan payments.
- Acting as a point of contact for insurers and members.
Importance of Regular Contributions
Regular contributions from both the employer and employees or members are necessary to maintain the group health insurance plan. Here's why:
- The employer's contribution indicates their commitment to the group's well-being and financial stability.
- Employee contributions ensure affordability and accessibility of group health insurance.
- Regular payments keep the plan active and guarantee continued coverage.
- Consistent contributions enable the employer or organization to renegotiate and modify the plan as needed.
Group Health Insurance Coverage
Group health insurance typically covers a wide variety of medical conditions and procedures, providing financial assistance for policyholders and their dependents. However, it is crucial to identify and understand the medical conditions and procedures covered by this type of insurance, as well as any potential limitations or exclusions.
Furthermore, different types of group health insurance plans offer different levels and scopes of coverage.
Medical Conditions and Procedures Covered
Group health insurance policies usually provide coverage for various medical services and treatments, such as:
- Inpatient and outpatient hospital services
- Professional services by physicians and other healthcare providers
- Diagnostic tests and imaging services
- Prescription medications
- Mental health and substance abuse services
- Rehabilitation services, such as physical therapy and occupational therapy
Limitations and Exclusions
Group health insurance policies often have certain limitations and exclusions. These may include:
- Pre-existing conditions, which may not be covered or may be subject to waiting periods
- Experimental or investigational treatments
- Cosmetic procedures
- Services related to obesity or weight loss, unless deemed medically necessary
- Alternative or complementary medicine
- Dental and vision care, although some policies may offer limited coverage for these services
Comparing Coverage Across Different Types of Group Health Insurance Plans
Different types of group health insurance plans provide varying levels and scopes of coverage. Here is a comparison of some common types of group health insurance plans:
| Type of Plan | Coverage |
|---|---|
| Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) | HMOs typically offer a lower cost but a more limited provider network. Referrals from a primary care physician are generally required for specialty care. |
| Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) | PPOs typically offer a broader provider network and greater flexibility but may have higher out-of-pocket costs. Referrals are not typically required. |
| Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) | EPOs offer a more limited provider network, similar to HMOs, but without the requirement for referrals. Out-of-network care is usually not covered. |
| Point of Service (POS) | POS plans combine features of HMO and PPO plans, allowing flexibility with higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care. |
Group Health Insurance Costs
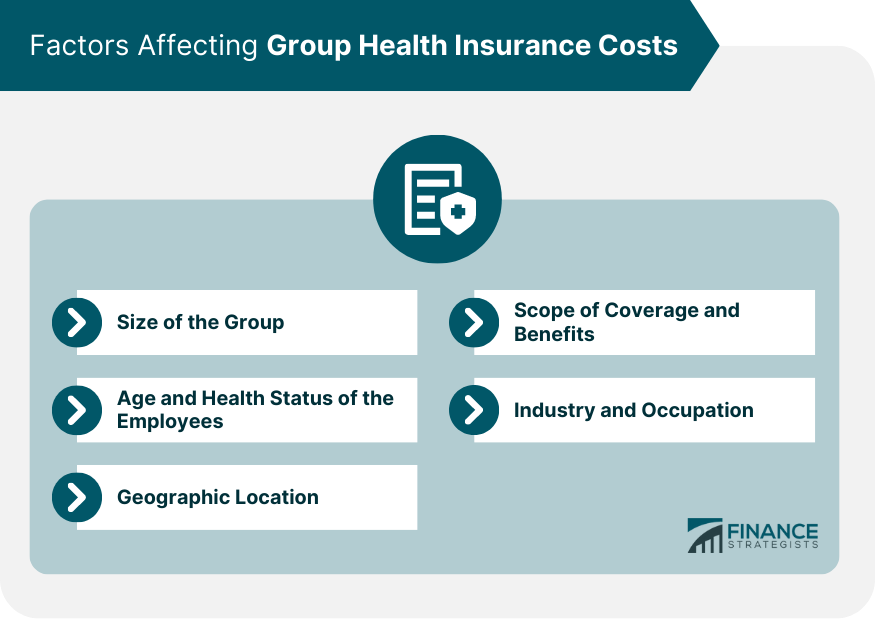
Group health insurance costs are influenced by several factors, which can vary depending on the type of plan and the insurer
Factors Affecting Group Health Insurance Costs
-
Employee demographics such as age, gender, and location can impact premiums due to the varying levels of health risks associated with each demographic.
-
Plan design, including deductibles, co-pays, and covered services, can affect premiums. Plans with lower deductibles and broader coverage typically have higher premiums, while high-deductible plans tend to have lower premiums.
-
The number of employees participating in a group health plan, as well as their overall health status, can significantly impact premiums. Insurers usually offer discounts to employers with a higher number of employees that participate in the plan.
-
Insurer competition and administrative costs associated with managing a group health plan, as well as the area's cost of living and healthcare expenses, can also influence premiums.
Comparing Group Health Insurance Plan Costs
In general, there are three primary types of group health insurance plans: Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and Point of Service (POS) plans. Each type offers different levels of flexibility and costs. Here's a brief comparison:
| Plan Type | Cost | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|
| HMO | Low to moderate | Limited network of providers |
| PPO | Moderate to high | Access to a broad network of providers, with incentives for using in-network providers |
| POS | Moderate to high | Greater flexibility for using out-of-network providers at a higher cost |
Payment Methods for Group Health Insurance
Employers have several options when it comes to paying for group health insurance. Common methods include:
-
Premium Sharing:Employers and employees both contribute a percentage or fixed amount towards the premiums. This arrangement can lower the overall cost for each party.
-
Fully-Insured Plans:The employer pays a fixed premium based on the number of employees and their demographics, and the insurer assumes the risk. Employers can take advantage of tax deductions for premium payments in this case.
-
Self-Funded Plans:Employers pay for healthcare services directly, taking on the risks and rewards of managing a health plan. These plans may offer greater control over costs and flexibility but do not benefit from the same tax advantages as fully-insured plans.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Group Health Insurance
Group health insurance is a popular choice for many businesses and organizations. It offers several benefits, but there are also some drawbacks to consider. In this section, we will explore the pros and cons of group health insurance, and compare it with individual health insurance.
Advantages of Group Health Insurance
- Cost-effective:Group health insurance typically costs less per person than individual health insurance. This is because the risk is spread across a larger pool of people, reducing the overall cost.
- Easy enrollment:Employees can easily enroll in group health insurance through their employer. This eliminates the need for individual applications and medical underwriting.
- Comprehensive coverage:Group health insurance plans often offer more comprehensive coverage than individual plans. This includes preventive care, mental health services, and prescription drugs.
- Tax benefits:Employers can deduct the cost of group health insurance as a business expense. Employees may also receive tax benefits, such as excluding the cost of premiums from their taxable income.
- Retention and recruitment tool:Offering group health insurance can help businesses retain and attract employees. This is because employees value the peace of mind and financial security that comes with health insurance.
Disadvantages of Group Health Insurance
- Limited choice:Employees may have limited choice in terms of providers and plans. This is because employers typically choose the plan and negotiate rates with the insurance company.
- Cost-sharing:Employees may be required to share the cost of premiums, deductibles, and copayments. This can make health insurance more expensive for employees, especially if they have a low income.
- Lack of portability:Group health insurance is typically tied to employment. This means that employees may lose their coverage if they leave their job or are laid off.
- Dependence on employer:Employees are dependent on their employer to provide health insurance. This can create a power imbalance, where employees feel they cannot leave their job because they would lose their health insurance.
Group Health Insurance vs. Individual Health Insurance
| Group Health Insurance | Individual Health Insurance |
|---|---|
| Cost-effective | More expensive |
| Easy enrollment | More complicated enrollment process |
| Comprehensive coverage | Less comprehensive coverage |
| Tax benefits for employer and employee | No tax benefits for employer |
| Limited choice | More choice in providers and plans |
| Cost-sharing | Less cost-sharing |
| Lack of portability | Portable coverage |
| Dependence on employer | No dependence on employer |
In conclusion, group health insurance offers several advantages, such as cost-effectiveness, easy enrollment, comprehensive coverage, tax benefits, and retention and recruitment tool. However, it also has some drawbacks, such as limited choice, cost-sharing, lack of portability, dependence on employer. When compared with individual health insurance, group health insurance is generally more cost-effective, but has limited choice and is tied to employment.
Individual health insurance, on the other hand, offers more choice in providers and plans but is more expensive and not tied to employment.
Group Health Insurance Administration
Group health insurance management involves the administration of health insurance policies for a group of people, typically in a workplace or association. This process ranges from enrollment, premium collection, claims processing, to ensuring regulatory compliance. The scale and complexity of responsibilities necessitate efficient and organized management.
Process of managing group health insurance
Managing group health insurance involves several key steps:
- Enrollment:Employees or members are informed about the plan, eligible dependents, and enrollment deadlines. New hires or members may have an additional enrollment window.
- Premium Collection:The employer or association coordinates premium payments to the insurance provider. In some cases, a third-party administrator (TPA) handles this process.
- Claims Processing:Employees or members submit medical bills to the insurance provider or TPA. These are then reviewed and paid according to the policy terms.
- Compliance:The employer or association must ensure annual compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, such as renewals and reporting.
Role of third-party administrators in group health insurance administration
Third-party administrators (TPAs) play a significant role in group health insurance administration. TPAs are external companies hired by the employer or association to manage specific aspects of the health insurance plan. Their responsibilities can include:
- Claims processing
- Premium collection
- Member services, like answering questions about the plan or processing changes
- Network management, such as negotiating contracts with healthcare providers
- Cost containment, such as implementing programs to reduce healthcare expenses
Legal and regulatory considerations in group health insurance administration
Group health insurance administration involves adhering to various legal and regulatory requirements:
- Affordable Care Act:Employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent employees must offer affordable coverage that meets minimum essential benefits. Failure to comply may result in penalties.
- ERISA:The Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 sets standards for employee benefits, including group health plans. It requires plan documents, reporting, and participant disclosures.
- HIPAA:The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act established privacy rules for medical records and patient information.
- State-specific requirements:Each state has its own insurance regulations and mandates, such as essential health benefits and rating restrictions. Employers must ensure their plans comply.
Group Health Insurance Trends
The health insurance industry is constantly evolving, and group health insurance plans are no exception. In recent years, employers and insurers have been adapting to shifting employee expectations, rising costs, and new technologies. Let's explore these developments and discuss their impact on the group health insurance market.
Telemedicine and Virtual Care
With the rise of telemedicine, group health insurance plans increasingly incorporate virtual care options to improve accessibility and affordability. Virtual consultations, mental health services, and remote monitoring are becoming standard features. This shift not only helps contain costs but also improves employee satisfaction by offering convenient, on-demand care.
Personalized Benefits and Wellness Programs
Customization is a growing trend as employers increasingly recognize that one-size-fits-all plans do not meet the diverse needs of their workforce. Tailored benefits and wellness initiatives offer targeted support for specific health concerns, promoting better overall health and reducing absenteeism.
This approach also bolsters employee satisfaction and loyalty by demonstrating a commitment to their well-being.
High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) and Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
As a cost-containment strategy, more employers are offering HDHPs with HSAs. These plans typically have lower premiums but higher deductibles. Employees use HSAs to pay for qualified medical expenses, which can be rolled over year after year. The combination of an HDHP and an HSA can lead to reduced overall insurance costs and increased employee engagement in health care decision-making.
Mental Health Parity
Mental health parity—ensuring equal coverage for mental and physical health conditions—is increasingly becoming a standard feature in group health insurance plans. Mental health coverage has historically lagged behind physical health coverage, and the push for parity reflects changing attitudes toward mental health as well as regulatory requirements.
Transparency and Data-Driven Decisions
Greater transparency and data-driven decision-making are transforming the group health insurance market. Cost transparency tools empower employees to make informed decisions about care providers, while data analytics enable employers to identify trends and optimize their insurance offerings.
Looking Ahead
As the health care landscape continues to change, group health insurance plans will need to respond accordingly. Employers should look for opportunities to incorporate new technologies, maximize value, and support the diverse needs of their employees. By staying informed and adapting to emerging trends, employers can provide competitive, cost-effective, and attractive health insurance benefits.
Closing Notes
Group health insurance plays a vital role in maintaining the health and well-being of employees, providing them with peace of mind and security. The knowledge you have gained from this guide should prove invaluable in navigating the complex landscape of group health insurance.
Remember, understanding the ins and outs of group health insurance can ensure your organization's benefits package remains competitive and attractive to top talent.