Understanding Health Insurance Costs: A Comprehensive Guide
Health insurance cost is a topic that affects millions of people worldwide. With rising healthcare expenses, understanding the factors that contribute to health insurance costs is essential. This guide aims to provide a clear and concise overview of health insurance costs, their key components, and strategies for reducing them.
Health insurance costs can be influenced by various factors, including deductibles, coinsurance, copayments, and provider networks. In this guide, we will delve into these factors and provide insights into the impact they have on overall health insurance costs. We will also explore strategies for reducing health insurance costs, including shopping around for plans, negotiating rates, and maximizing the use of preventive care.
Understanding Health Insurance Costs
Health insurance costs can be confusing, but understanding the key components can help you make informed decisions. Health insurance costs generally consist of premiums, deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments.
Health Insurance Premiums
A health insurance premium is a fixed amount you pay monthly or annually, regardless of whether or not you use medical services. Premiums vary based on a number of factors, including your age, location, and the type of coverage you choose.
Insurers calculate premiums by considering the cost of medical services, administrative expenses, and the number of policyholders.
Deductibles, Coinsurance, and Copayments
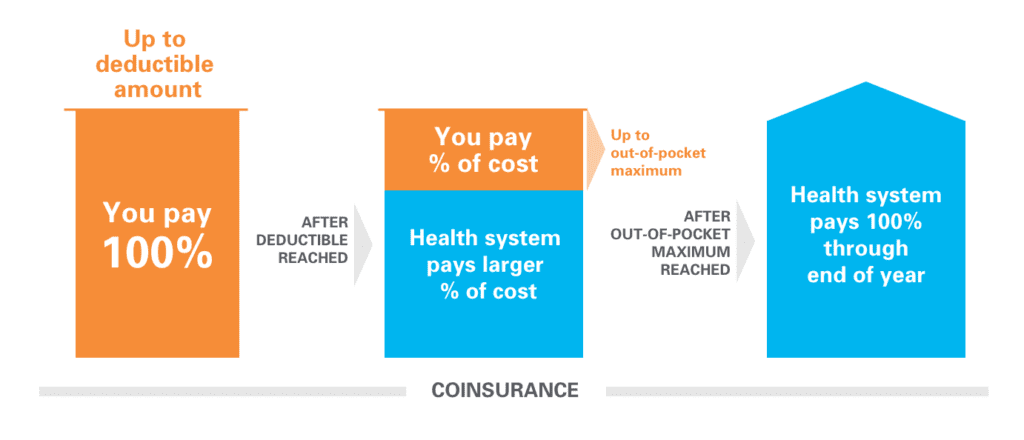
Deductibles are the amount you pay out-of-pocket for medical services before your insurance starts covering costs. Coinsurance is the percentage of costs you pay after reaching your deductible, while copayments are fixed fees you pay for specific services. Higher deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments generally lead to lower premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs when you need medical care.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Premiums
Several factors can influence health insurance premiums. In addition to the cost of medical services and administrative expenses, insurers consider:
- Your age: Older individuals typically have higher premiums due to increased healthcare needs.
- Your location: Premiums vary by state and city due to differences in cost of living and medical costs.
- Your health status: Pre-existing conditions or chronic illnesses can lead to higher premiums.
- Your lifestyle: Tobacco use, high-risk behaviors, or occupations can result in higher premiums.
- The type of coverage: Comprehensive plans typically have higher premiums than basic plans.
Understanding health insurance costs is essential for making informed decisions about your coverage. By familiarizing yourself with the key components of health insurance costs and the factors influencing premiums, you can choose a plan that meets your needs and budget.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Understanding the types of health insurance plans available is crucial for making informed decisions about your healthcare coverage. With varying levels of coverage, provider networks, and cost structures, it's essential to weigh the options to find the best fit for your needs.
This section focuses on four primary plan types: HMO, PPO, POS, and EPO plans.
HMO (Health Maintenance Organization)
HMO plans typically have lower monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to other plan types. However, they usually come with a smaller provider network. With an HMO plan, you'll need to choose a primary care physician (PCP) to coordinate your care, and you may need a referral to see specialists.
Monthly premium
$200-$300 (varies based on coverage and location)
Deductible
$0-$500 (often lower compared to other plans)
Coinsurance
Typically a set percentage (e.g., 10-20%) after the deductible is met
Out-of-pocket maximum
$1,500-$6,500 (lower compared to other plans)
PPO (Preferred Provider Organization)
PPO plans usually offer a larger provider network and more flexibility than HMO plans. While PPOs tend to have higher monthly premiums, they allow you to see specialists without a referral and offer more out-of-network coverage, albeit at a higher cost.
Monthly premium
$300-$450 (varies based on coverage and location)
Deductible
$500-$1,000 (higher compared to HMOs)
Coinsurance
Typically a set percentage (e.g., 10-25%) after the deductible is met
Out-of-pocket maximum
$3,000-$7,000 (higher compared to HMOs)
POS (Point of Service)
POS plans combine elements of HMO and PPO plans. They typically offer a smaller network of preferred providers, like HMOs, and allow you to see out-of-network providers, like PPOs. However, out-of-network services are more expensive with POS plans.
Monthly premium
$250-$400 (varies based on coverage and location)
Deductible
$500-$1,500 (similar to PPOs)
Coinsurance
Typically a set percentage (e.g., 10-25%) after the deductible is met
Out-of-pocket maximum
$3,000-$6,500 (similar to PPOs)
EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization)
EPO plans generally provide a moderate-sized network of preferred providers. EPOs require you to stay within the network for coverage, much like HMOs, but without the need for a PCP or referrals.
Monthly premium
$250-$350 (varies based on coverage and location)
Deductible
$500-$1,000 (similar to PPOs)
Coinsurance
Typically a set percentage (e.g., 10-20%) after the deductible is met
Out-of-pocket maximum
$3,000-$6,500 (similar to PPOs and POS plans)The level of coverage and provider network can significantly impact the cost of health insurance plans. Plans with broader provider networks and more flexible coverage options typically come with higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
At the same time, plans with more restrictive networks and coverage requirements usually have lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs. Consider your healthcare needs and preferences when choosing the right plan type for you.
Average Health Insurance Costs
Average health insurance costs in the United States often vary by type of plan, individual or family status, and location. In recent years, these costs have risen significantly, causing concern for many consumers and employers. In this section, we will delve into the details of these costs, their trends, and how they compare across different states and plan types.
National Average Health Insurance Costs
According to data from Kaiser Family Foundation, the average annual health insurance premium for employer-sponsored family plans in 2020 was $21,342, while the average for individuals was $7,470. This represents an increase of 4% and 2% respectively from the previous year, demonstrating a consistent upward trend over the past decade.
Comparing Costs for Individuals, Families, and Employers
Individual health insurance plans, which are not employer-sponsored, typically have lower premiums than family plans. For example, in 2020, the average individual premium was $456 per month, while the average for a family plan was $1,782. These figures, however, do not reflect the potential impact of subsidies or cost-sharing reductions that may lower the actual out-of-pocket expenses for eligible individuals
In 2020, employers contributed an average of 72% of the premium for single coverage and 65% for family plans. The increasing costs of health insurance have led some employers to either reduce the percentage of premiums they cover or to pass on the entire premium increase to their employees.
Trends in Health Insurance Costs Over the Past Decade
Health insurance costs have climbed remarkably over the past decade. The following table illustrates the rising trend of health insurance costs from 2011 to 2020.
| Year | Average Premium for Single Coverage | Average Premium for Family Coverage |
| 2011 | $5,065 | $13,862 |
| 2016 | $6,435 | $18,142 |
| 2020 | $7,470 | $21,342 |
Average Health Insurance Costs by State and Plan Type
Here, we provide a table comparing average health insurance costs by state and plan type (employer-sponsored and individual marketplace plans) for the year 2020, based on eHealth's 2020 Health Insurance Price Index.
| State | Average Employer-Sponsored Premium (Family) | Average Individual Marketplace Premium (Family) |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $17,233 | $15,456 |
| California | $20,768 | $19,234 |
| Florida | $17,640 | $15,537 |
| Georgia | $19,010 | $16,048 |
| Illinois | $17,295 | $19,882 |
| New York | $21,366 | $18,730 |
| Texas | $18,553 | $16,575 |
The above table highlights the substantial difference between employer-sponsored plan premiums and individual marketplace plan premiums in each of the featured states. These variations are influenced by factors such as state regulations, subsidies, competition among insurers, and regional healthcare costs.
Strategies to Reduce Health Insurance Costs
Health insurance costs can be a significant financial burden for many individuals and families. However, there are strategies you can employ to lower these costs. By shopping around for plans, negotiating rates, maximizing preventive care, and exploring high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) and health savings accounts (HSAs), you can make health insurance more affordable.
Additionally, lifestyle choices play a crucial role in health insurance costs, and government programs and subsidies can provide further assistance.
Shopping Around for Plans
To find the most affordable health insurance plan, it's essential to compare options from multiple providers. Consider factors such as premiums, deductibles, copayments, and coverage limits. Online marketplaces, such as HealthCare.gov, can help you compare plans and enroll in coverage.
Negotiating Rates
Health care providers often have some flexibility in the rates they charge for services. By negotiating rates, you may be able to reduce your out-of-pocket costs. Consider seeking help from a healthcare advocate or consultant to negotiate on your behalf.
Maximizing Preventive Care
Preventive care can help you maintain good health and avoid costly medical treatments. Many health insurance plans cover preventive services, such as vaccinations, screenings, and wellness exams, at no cost to you. Take advantage of these services to lower your overall healthcare expenses.
High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) and Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
HDHPs typically have lower premiums but higher deductibles than traditional health insurance plans. Pairing an HDHP with an HSA can help you save money on healthcare costs. HSAs allow you to set aside tax-free funds for medical expenses, and these funds can roll over from year to year.
Note:To be eligible for an HSA, you must have an HDHP and cannot be enrolled in Medicare or claimed as a dependent on someone else's tax return.
Lifestyle Choices and Health Insurance Costs
Healthy lifestyle choices can significantly impact your health insurance costs. For example, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and practicing regular exercise can lower your premiums and reduce the likelihood of developing chronic conditions.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity can lead to various health issues, such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. By managing your weight, you can reduce the risk of these conditions and lower your health insurance costs.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking increases the risk of numerous health problems, including lung cancer, heart disease, and stroke. In addition to the numerous health benefits of quitting, many insurers offer lower premiums to nonsmokers.
- Regular exercise: Regular physical activity can help prevent obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and other health conditions. Many insurers offer discounts or rewards for participating in wellness programs that encourage exercise.
Government Programs and Subsidies
Various government programs and subsidies can help reduce health insurance costs. For example, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) offers premium tax credits and cost-sharing reductions to eligible individuals enrolling in marketplace plans. Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) provide coverage to low-income families and children.
Additionally, some states have implemented reinsurance programs to lower premiums for individual market plans.
Note:Eligibility for government programs and subsidies depends on factors such as income, family size, and citizenship status. Visit HealthCare.gov or your state's marketplace to learn more about available options.
Comparing Health Insurance Costs Across Borders

Health insurance costs in the United States often draw comparisons to other developed countries. These comparisons allow for a greater understanding of how health insurance costs are influenced by various factors and how different healthcare systems impact these costs.
Health Insurance Costs in the United States vs. Other Developed Countries
According to the Commonwealth Fund's International Health Policy Survey, the United States has the highest healthcare spending per capita among developed countries, with an average of $10,966 per person in 2019. In comparison, countries such as the United Kingdom, Canada, Germany, and Australia spent significantly less, with per capita health spending ranging from $4,945 in the United Kingdom to $6,129 in Germany.This discrepancy in spending may be attributed to several factors, including the financing and organization of healthcare systems, the utilization of healthcare services, and the costs of medical goods and services.
Factors Contributing to Differences in Health Insurance Costs
1. Financing and Organization of Healthcare Systems
The United States relies heavily on private insurance and out-of-pocket payments for healthcare financing, which often results in higher costs compared to countries with universal healthcare systems.
2. Utilization of Healthcare Services
The U.S. healthcare system has a greater focus on specialty and high-technology care, resulting in higher utilization and costs compared to other developed countries.
3. Costs of Medical Goods and Services
The United States pays more for pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and physician and hospital services than other developed countries. This is due in part to the lack of price controls and negotiations in the U.S. market.
Examples of Universal Healthcare Systems and Their Impact on Health Insurance Costs
universal healthcare systems, such as those found in the United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia, have the government as the primary payer for healthcare services. This allows these countries to negotiate lower prices for medical goods and services, leading to lower overall health insurance costs compared to the United States.
In the United Kingdom's National Health Service, for example, physicians are salaried, which eliminates the need for billing and administrative costs. Additionally, the government negotiates prices for pharmaceuticals and medical devices, further reducing costs.
In Canada, the single-payer system, known as Medicare, covers the majority of healthcare services, with Canadians paying minimal out-of-pocket costs. Canada's universal healthcare system results in lower administrative costs compared to the United States, contributing to lower overall health insurance costs.Australia's healthcare system, called Medicare, combines public and private financing.
The government's bulk-billing system, in which doctors are paid a set fee for services, helps reduce out-of-pocket costs for patients. This system, along with the government's regulation of healthcare prices, contributes to lower overall health insurance costs in Australia.
The differences in healthcare systems and health insurance costs between the United States and other developed countries illustrates the importance of considering various factors, including financing and organization, utilization, and the costs of medical goods and services, when comparing health insurance costs across borders.
Epilogue
In conclusion, health insurance costs are a complex and multifaceted topic that requires careful consideration and understanding. By identifying the factors that contribute to health insurance costs, comparing the costs of different health insurance plans, and exploring strategies for reducing costs, individuals and families can make informed decisions about their health insurance coverage.
Remember, a little knowledge can go a long way in reducing health insurance costs and ensuring access to quality healthcare.